Bolted Motor Mount
1. Scope & Design Constraints
Objective: Engineer a structural interface to secure the powertrain's electric motor (240 Nm peak torque) to the tubular spaceframe chassis.
Constraints:
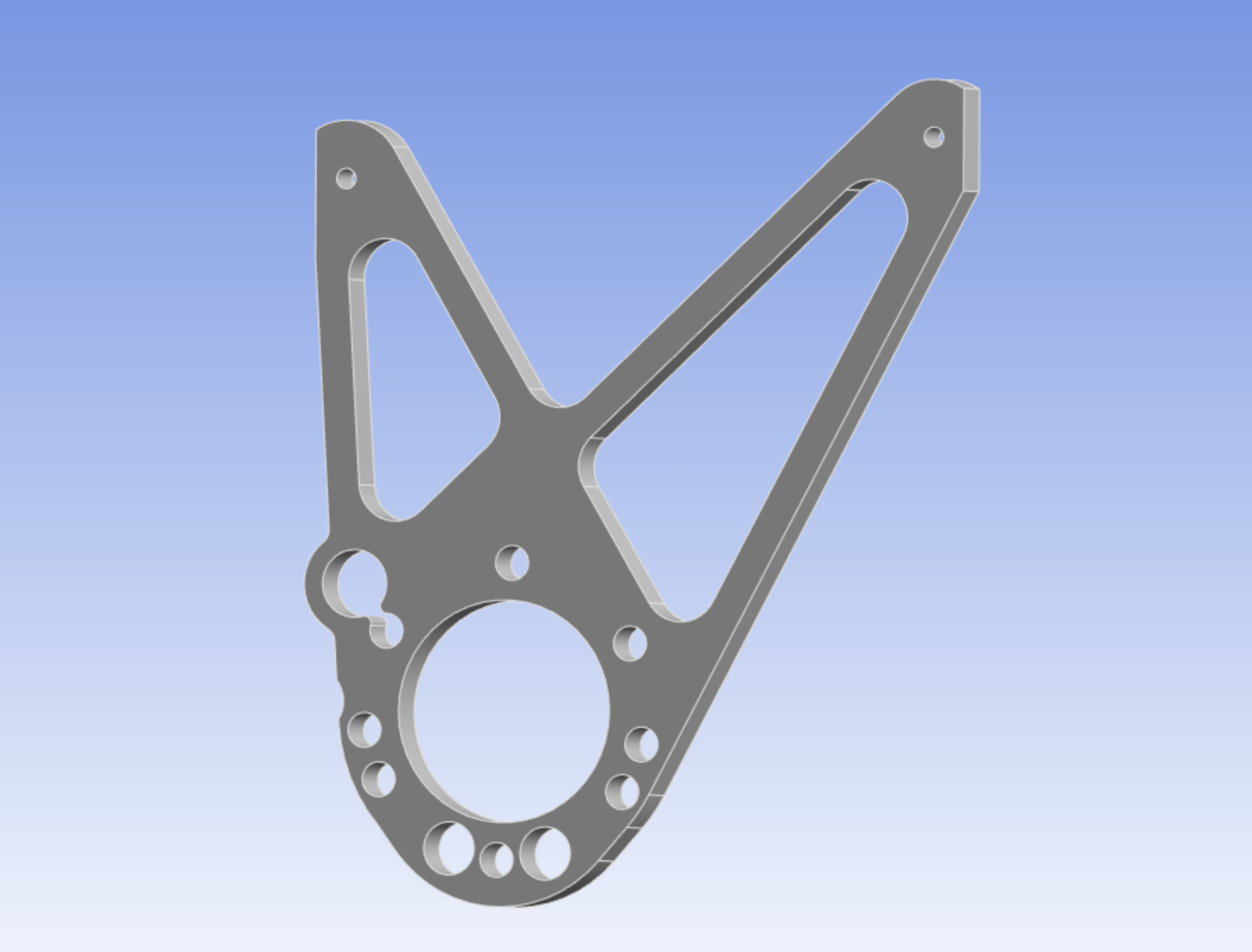
DFM: Component restricted to planar geometry for rapid waterjet manufacturing (0.5" 6061-T6 Aluminum).
Strength: Must be able to resist 2.37 kN of compressive load.
Reliability: Minimum Factor of Safety (FOS) of 2.0 required.
The mount integrated into the vehicle assembly, interfacing between the electric motor and rear chassis subframe.
2. Analytical Load Derivation
Prior to CAD modeling, I quantified the loading conditions using first-principles analysis.
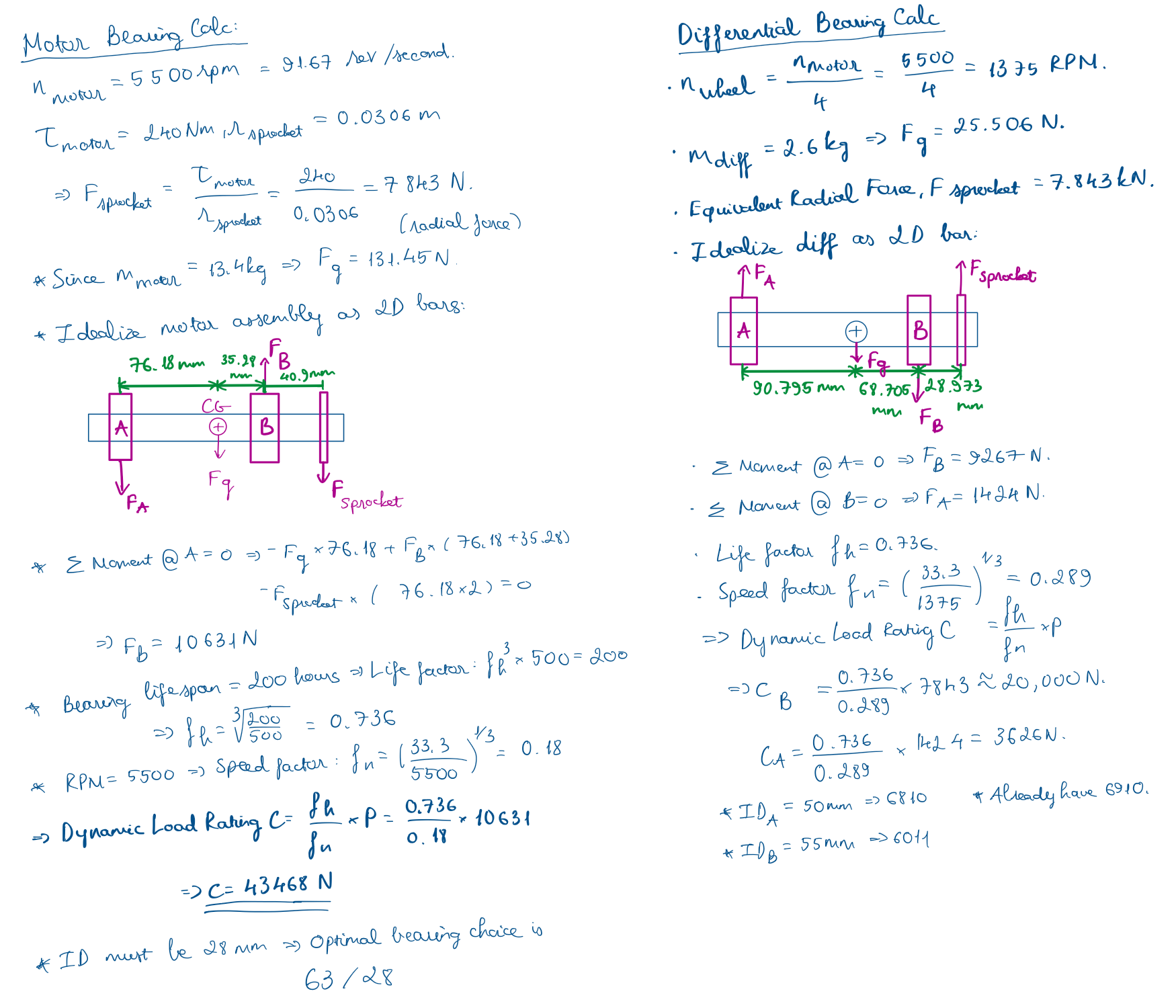
Global Equilibrium: Resolved motor torque and chain tension into a net radial reaction force of $2.37$ kN via Free Body Diagrams.
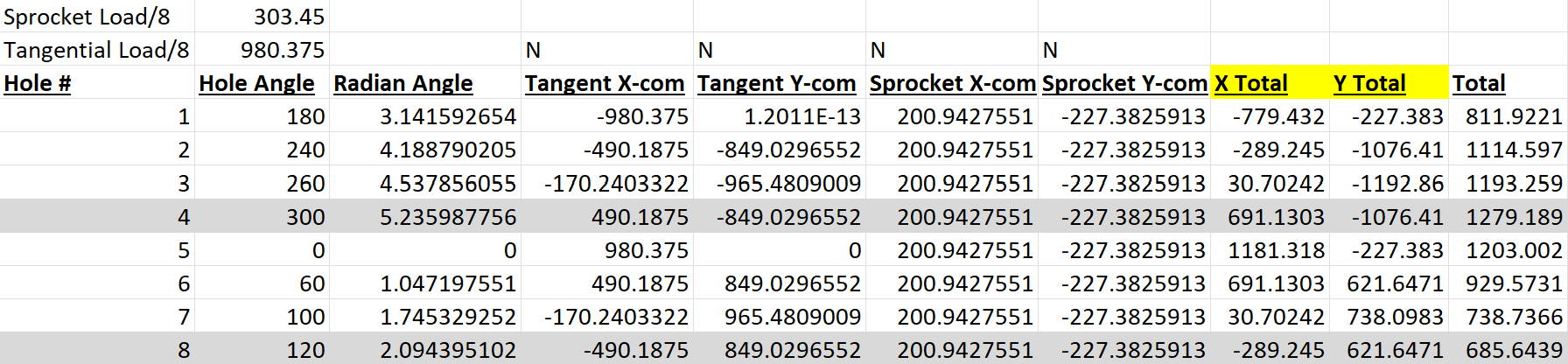
Vector Analysis: Developed a parametric Excel calculator to perform a Bolt Group Analysis. This tool resolved shear vectors for the eccentric 8-bolt pattern ($0^\circ$ to $300^\circ$) to identify the critical load case for fastener sizing.
The calculation of loads on each motor bolts.
3. Design & Topology Optimization
Utilizing SolidWorks, the geometry was refined through 7 iterations focused on maximizing the stiffness-to-weight ratio.
Mass Reduction: Reduced component weight by $9\%$ (from $0.8$ lbs to $0.72$ lbs) through manual topology optimization, removing non-structural mass while reinforcing primary load paths.
Geometry: Maintained a strictly 2.5D profile to eliminate CNC milling requirements and reduce manufacturing lead time.
FEA of the latest 6 iterations. The shape changed to accommodate different motor’s placements and bolt clearances.
4. FEA Validation & Fastener Selection
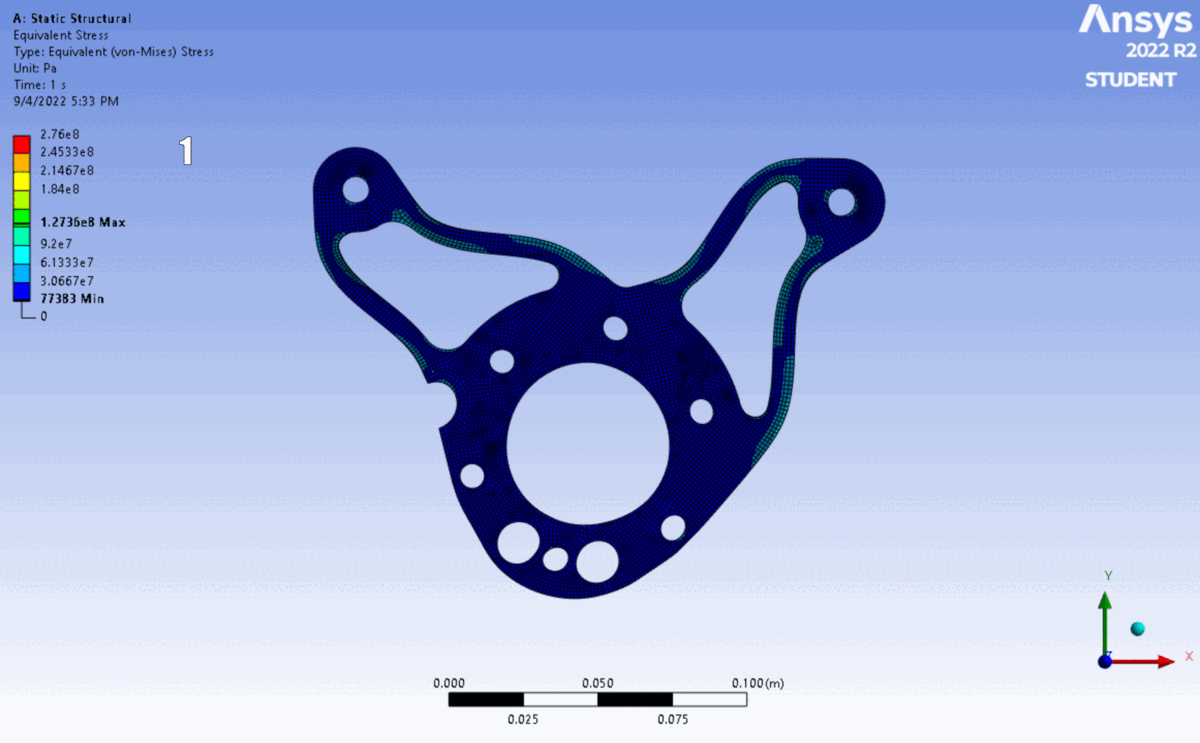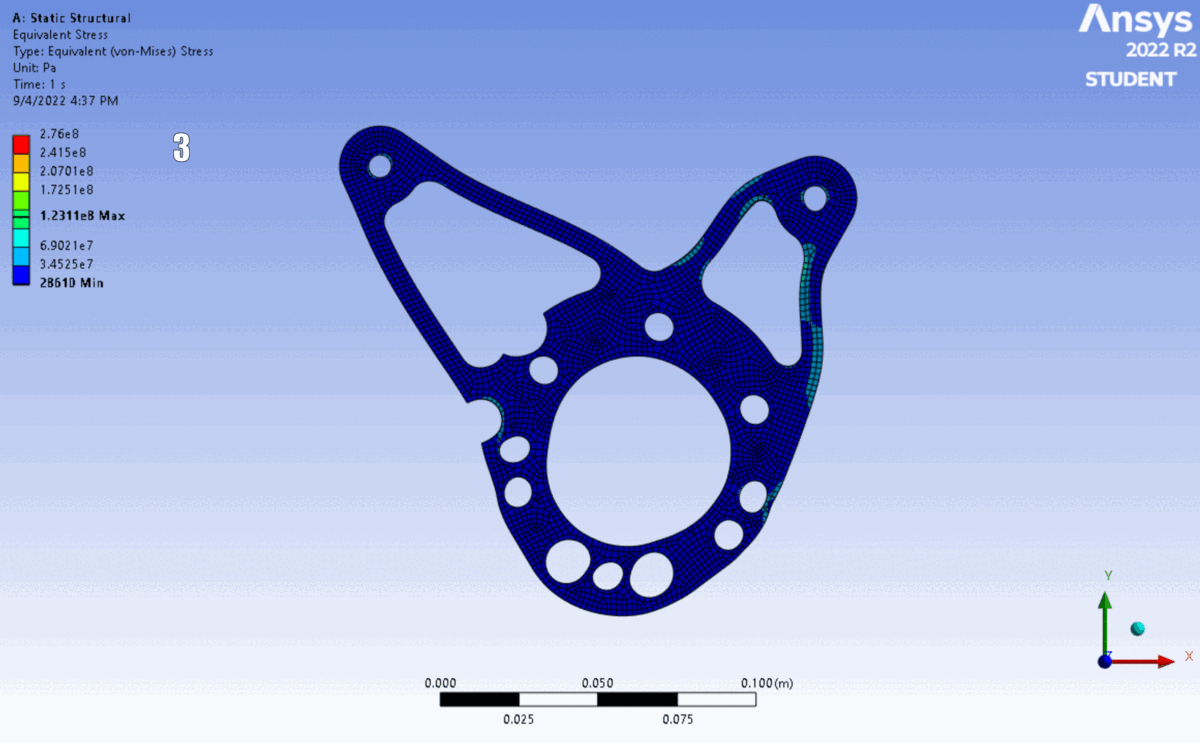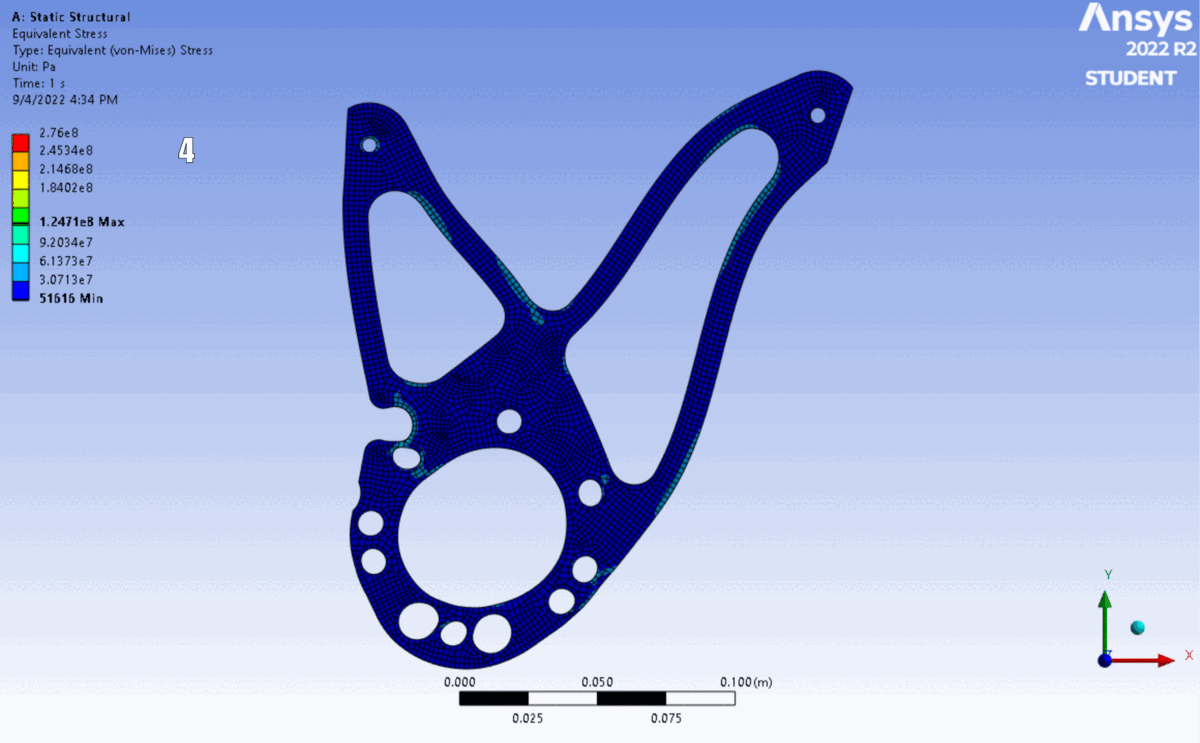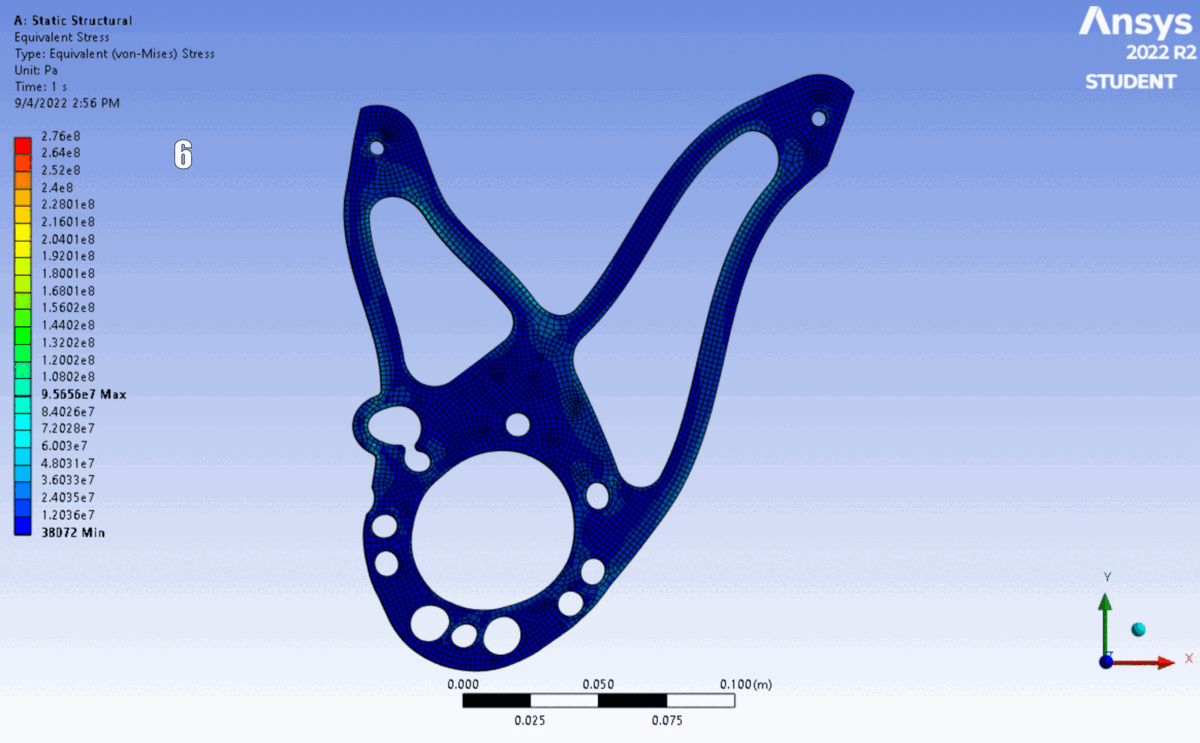
The design was validated using ANSYS Mechanical (Static Structural) to verify performance against yield.
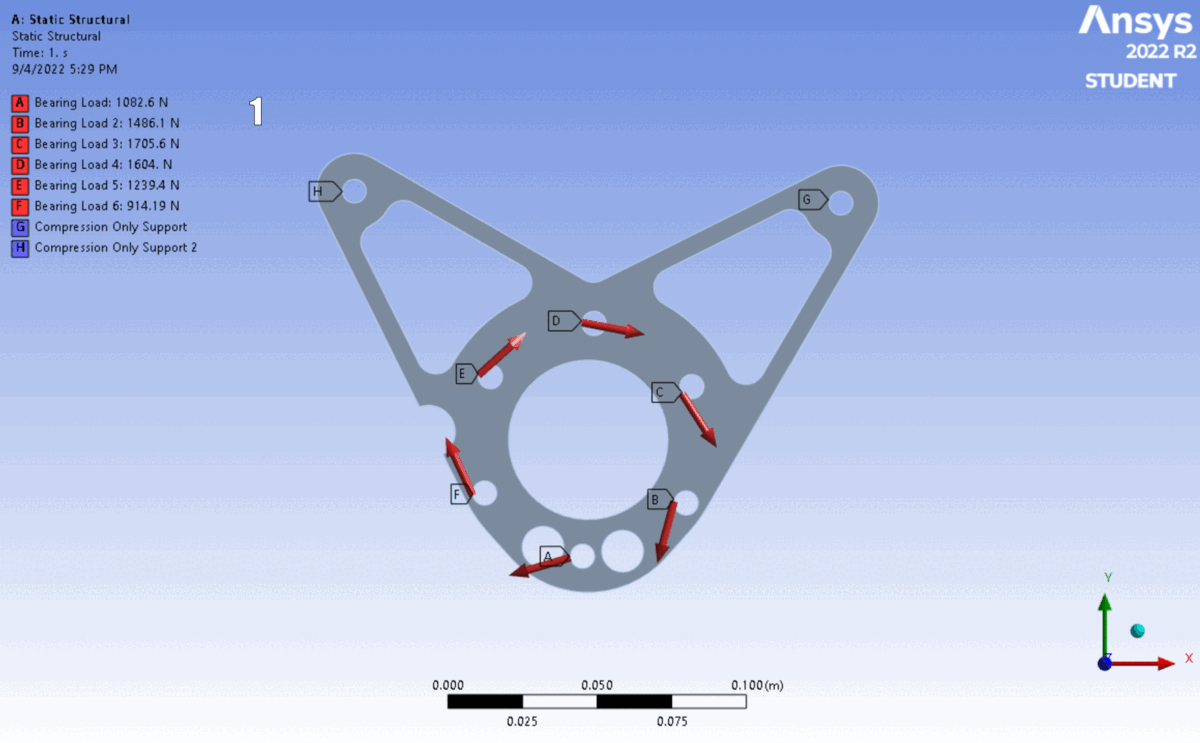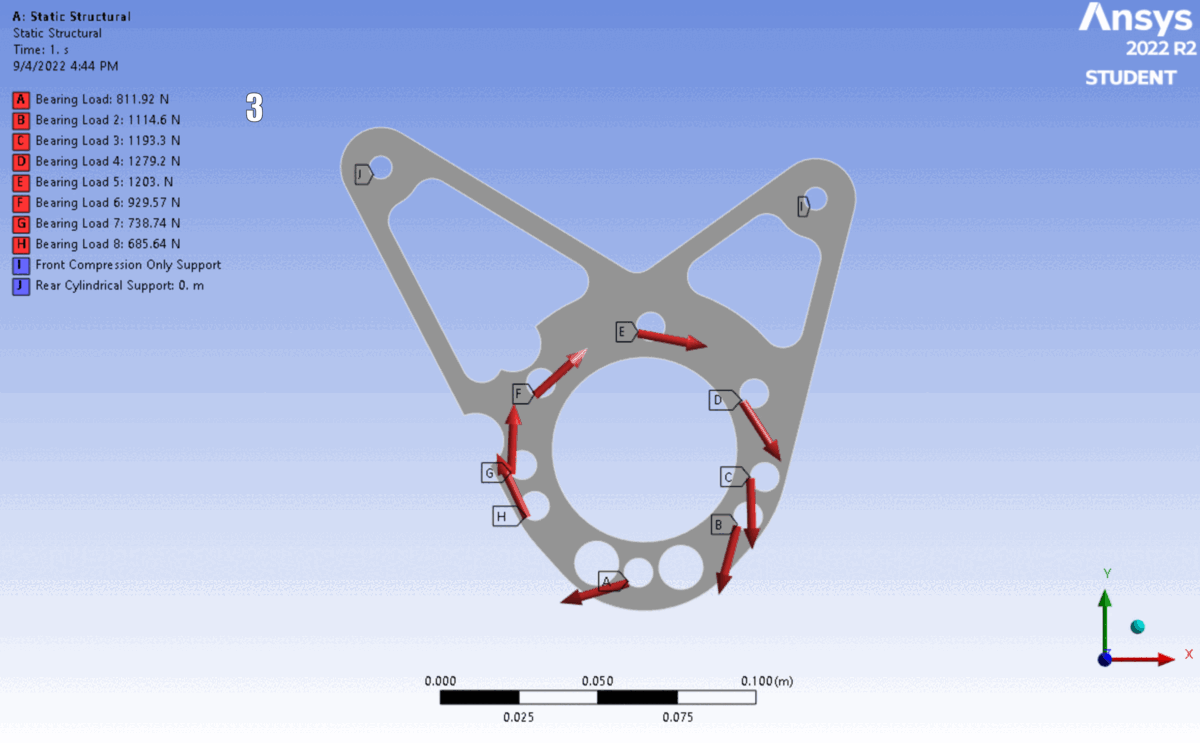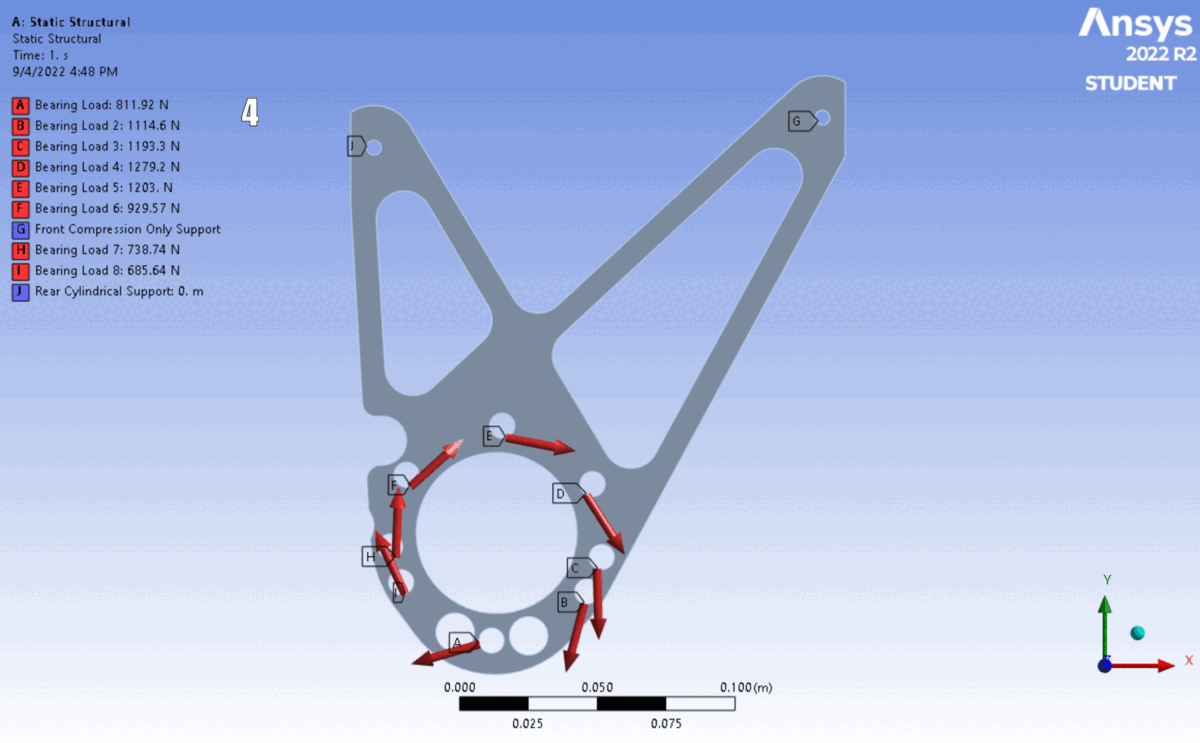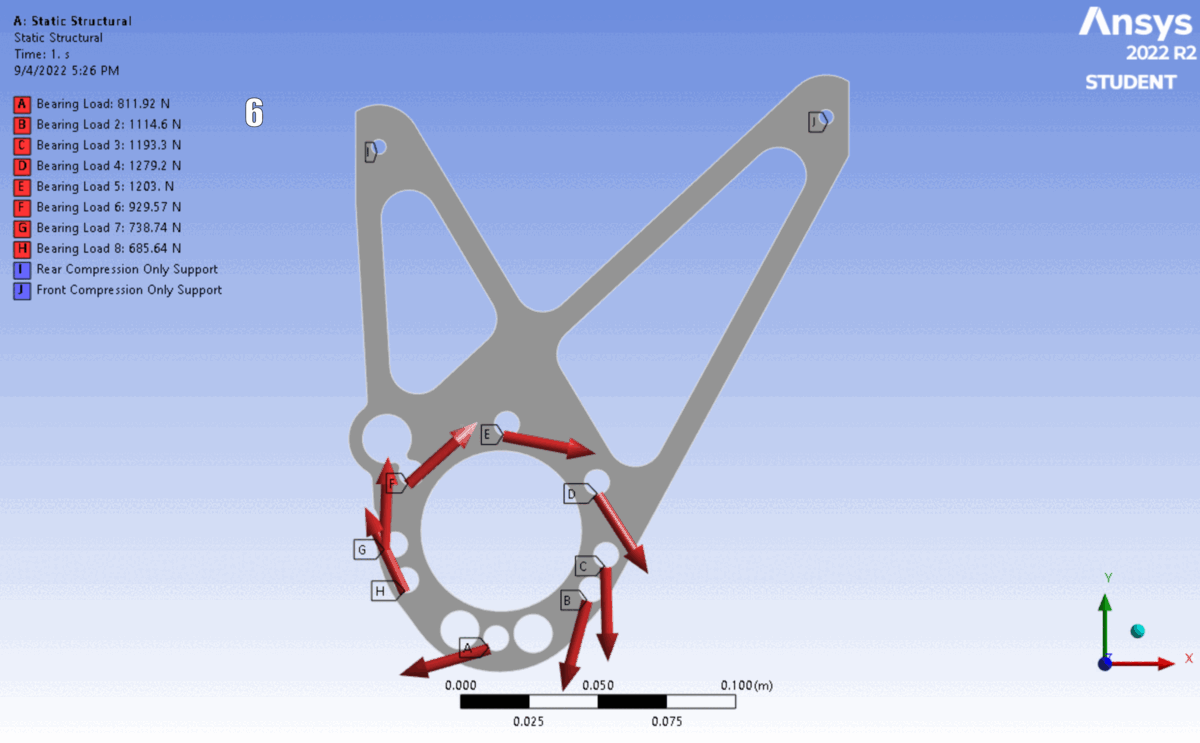
Simulation: Applied calculated reaction forces as remote loads distributed across bearing surfaces, with fixed supports at chassis mounting points.
Results: Simulation confirmed a minimum Factor of Safety of $2.90$, providing a robust margin for dynamic shock loading.
Fastener Selection: Selected AN3 aviation bolts based on the calculated peak shear vector, ensuring compliance with competition regulations.
5. Manufacturing & Outcome
The final design was waterjet cut from 6061-T6 plate and successfully integrated into the vehicle, meeting all mass and stiffness targets.
Technical Summary
Role: Mechanical Design Engineer
Analysis: Rigid Body Dynamics, Bolt Group Vector Analysis, Static Structural FEA.
Key Metric: $9\%$ Mass Reduction achieved while maintaining $2.9$ FOS.
Tools: SolidWorks, ANSYS Mechanical, Excel, SpaceClaim.